Geographical position

Republic of Serbia
General Information
After the division of ex- Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRJ) and civil war of 1991, the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was formed in 1992 consisting of two federal units: Serbia and Montenegro. At the session of the Parliament of FR Yugoslavia held on 5 February 2003 the Union of Serbia and Montenegro was announced. After the referendum conducted on the state status of the Republic of Montenegro, held on 21 May 2006 when the citizens of Montenegro voted for the independence of this republic, Serbia also became an independent state, the Republic of Serbia.
After 90 years the members of the Parliament of the Republic of Serbia voted the renewed independence on 5 June 2006. The new Constitution was announced on 8 November 2006 by the Parliament of the Republic of Serbia and it was adopted on 30 September 2006, and then approved on the referendum conducted on 28 and 29 October of the same year.
The Republic of Serbia covers the area of 88,361 km2 and has 7,440,769 inhabitants, the data for the Autonomous Province of Kosovo have not been included. The Republic of Serbia consists of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina and Autonomous Province of Kosovo. According to the Resolution of the United Nations Security Council No 1244, adopted on 10 June 1999 temporary civil administration of the United Nations (UNMIK) was established on the territory of Kosovo. The Government of Kosovo unilaterally declared the independence on 17 February 2008 which is not recognized by the Republic of Serbia.
Referring the national population structure the Serbs are the most present (apx 82%). Serbia borders Hungary to the north, Romania to the north-east, Bulgaria to the east, Macedonia and Albania to the south, Montenegro to the south-west, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina (Serb Republic) to the west. The border is 2,114.2 km long. The capital is Belgrade (1.6 million inhabitants), and larger cities are: Novi Sad, Niš, Kragujevac, Priština, Subotica, Zrenjanin, Kruševac, Užice, Pančevo, Šabac, Valjevo, Kraljevo...
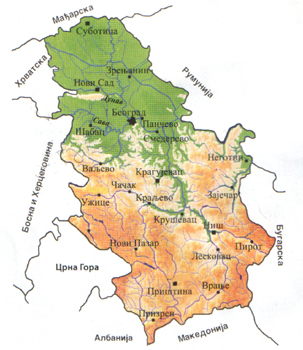
Geographical characteristics
A vast plain on the north through flat, hilly and mountainous areas, heights and high mountains south of the Sava and Danube, with wide spread valleys, gorges and ravines in between. The plains are found in the Pannonian area including: Mačva, Posavina, Pomoravlje, Stig and Negotin area in the eastern Serbia. Serbia has 55 % of arable land and 27% is covered with forests. There are several mountain ranges over 2,000 meters high, the highest peak is Midžor, 2169m
The rivers of Serbia flow into three seas: the Adriatic, Black and Aegean. The largest river is the Danube (navigable) with its tributaries the Sava (navigable), Tisa (navigable), Morava, Begej (navigable), Tamiš, Nišava, Timok, Kolubara, Ibar. Several artificial lakes have been created for power production. The largest of these are the Djerdap Lake, Zlatar Lake and Potpec.
Continental climate. The mean annual temperature of 11-12°C, precipitation 550-650mm a year.
Deciduous trees and some conifers vegetation of Central Europe. Mountain parts are with pasture. National parks: Fruška Gora, Tara, Zvijezda, Resava, Djerdap.
Serbia is located at an important traffic route of international significance: the Pannonian plain – Morava-Vardar Valley- the Aegean sea. The main communication hubs are Belgrade and Niš.

Economy
Industry and mining of the Republic of Serbia include mine and stone excavation, manufacturing industry and production and distribution of electrical energy, gas and water. Industry and mining companies employ 696,540 employees, i.e. 52 % of total employee number in the Republic of Serbia. Elektroprivreda /Electricity production/ of Serbia (EPS) includes coal mines, electricity energy resources (hydro power plants, thermo power plants), transmittance network and distribution system. Mining in Serbia is the basis of industry and consequently of the economy of our country. The most significant coal fields, including low calorie coal – lignite excavated in mining fields of Kolubara and Kostolac, as well as copper and precious metals which are present in the mining and smelt area of Bor. Secondary precious petal refining from copper is also significant.
The most developed agriculture branches are cattle breeding (43 percent) and farming (42 percent), followed by fruit growing and vintage (12 percent), and other crops, 3 percent. Agriculture land includes 5,734,000 hectares (0.56 ha per inhabitant), and about 4,867,000 hectares is arable land (0.46 ha per inhabitant).
 Skupstinagrada Zrenjanina
Skupstinagrada Zrenjanina